Employee Engagement Action Plan: Proven Tactics to Boost Workplace Motivation and Retention
Learn how to build a winning employee engagement strategy with actionable tips to enhance morale, foster motivation, and retain top talent in your workplace.
On this page
A well-structured employee engagement plan is no longer a “nice-to-have”—it’s a strategic necessity for organizations that want to boost morale, improve retention, and drive performance. Whether you're designing an employee engagement programme from scratch or fine-tuning an existing one, a clear engagement action plan can make all the difference.
By combining thoughtful planning with actionable steps, HR leaders can create a powerful employee engagement action plan that resonates across all levels of the organization. In this article, we explore how to develop an employee engagement strategy, share proven frameworks, and highlight practical ways to bring your engagement goals to life.
What does the stratistics say?
According to recent Gallup surveys, only 32% of full- and part-time employees in the U.S. are currently engaged, with an alarming 18% falling into the actively disengaged category.
This decline in engagement has given rise to a pressing concern for organizations, especially as the ratio of engaged to actively disengaged workers reaches its lowest point in almost a decade.
As businesses grapple with this unsettling trend, a parallel challenge arises: the struggle to retain talent.
A study involving over 600 U.S. businesses with 50-500 employees revealed that an overwhelming 63.3% find retaining employees more challenging than the initial recruitment process. In the wake of this predicament, over a third of the workforce is actively or casually seeking new job opportunities, culminating in a staggering $2.9 million per day spent by U.S. employers in their pursuit of replacement workers—amounting to a staggering $1.1 billion annually.
In the face of these challenges, the critical question arises: What does it take to retain top talent and rekindle the flame of employee engagement?
The answer lies not in merely fostering employee happiness or satisfaction but in the deliberate cultivation of a robust employee engagement planning. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of developing an effective action plan to reignite workplace engagement.
Importance of employee engagement in the workplace
Employee engagement is not merely a buzzword; it is a key driver of organizational success. Engaged employees are more likely to be motivated, enthusiastic, and aligned with the company's goals.
This alignment translates into tangible benefits, such as increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and a positive impact on the bottom line. Moreover, engaged employees act as ambassadors for the organization. They are more likely to speak positively about their workplace, contributing to a positive employer brand and attracting top talent.
Who is responsible for employee engagement action planning?
The responsibility for employee engagement action planning typically falls on a collaborative effort involving multiple stakeholders within an organization. While the specific structure and roles may vary from one organization to another, the following key players are often involved
1. Leadership/management team
Top-level executives, senior leaders, and managers play a crucial role in driving employee engagement. They set the tone for the organization's culture and are responsible for creating an environment that fosters engagement.
2. Human resources (HR) department
HR professionals often take a lead role in managing and facilitating employee engagement initiatives. They may conduct surveys, analyze data, and work with other departments to develop action plans based on feedback.
3. Managers and supervisors
Frontline managers and supervisors have direct contact with employees. They play a critical role in understanding individual and team dynamics, providing feedback, and implementing strategies to improve engagement at the team level.
4. Employee engagement teams or committees
Some organizations establish specific teams or committees dedicated to employee engagement. These groups may include representatives from different departments and levels of the organization.
5. Employees
Employee engagement is a two-way street, and employees themselves have a role in the action planning process. Their input, feedback, and involvement in the planning and implementation of initiatives are essential for success.
6. Internal communication teams
Effective communication is crucial for successful engagement initiatives. Internal communication teams are responsible for ensuring that information about engagement efforts is communicated clearly and reaches all employees.
7. Training and development teams
If skill development and training are identified as areas for improvement in engagement surveys, the training and development teams may be involved in crafting and implementing relevant programs.
8. Diversity and inclusion teams
In organizations that prioritize diversity and inclusion, these teams may be involved in ensuring that engagement initiatives are inclusive and address the needs of a diverse workforce.
The collaborative effort of these stakeholders helps ensure a holistic approach to employee engagement action planning, considering various perspectives and addressing the unique challenges and strengths within the organization. The specific roles and responsibilities may be outlined in an organization's overall strategic plan or HR policies.
How to design an employee engagement action plan?
Here is a step-by-step guide to designing an employee engagement action plan and running it end to end.
Step 1: Scan the internal environment of the organization
Scanning the internal environment constitutes studying the various ways the organization’s employees, management, stakeholders, business strategy, culture, resources, and capabilities engage with each other.
For instance, what are the different employee touchpoints that the leadership has with the employees? What are the different productivity tools used in the organization? How does the organization implement a business strategy? What are the various employment benefits offered? How often are outreach programs conducted by the leadership team?
HR needs to not only frame these questions that are unique to their organization but also self-evaluate the organization on how well they fare in each of these interactions.
The tools that can be used to conduct this study are:
- Group discussions
- Employee/ Stakeholder Interviews
- Employee surveys
- Resource data
- Performance reviews
- Feedback
- Employee surveys & pulse checks: Empuls makes it easy to run anonymous engagement and feedback surveys at regular intervals. You can analyze sentiment and trends to assess engagement levels and identify pain points across the organization.
- Employee NPS (eNPS): Quickly assess employee loyalty and advocacy using built-in eNPS tools.
- Analytics dashboards: Empuls offers real-time insights into engagement drivers and workforce mood, helping HR leaders understand internal strengths and weaknesses.
Step 2: Scan the external environment of the organization
The external environment of an organization consists of the competitive, economic, political, socio-cultural, and technological landscape of the market the organization is working in. These are important to be taken into consideration in framing an annual employee engagement program. These affect the effectiveness of all strategic initiatives.
Abhijit Bhaduri, author of the best seller ‘The Digital Tsunami’ mentions how technology trends like Augmented Reality and Holography can be effectively used in job simulation and employee experience. Thus having a careful watch on changing competitive benchmarks, industry trends, digital tools for employee engagement, etc and prove useful to reinvent a program to create an engaged workforce.
The following tools can be used to conduct this scan:
- Market research
- Benchmarking
- Competitor analysis
- Trend analysis
The expected outcome of this step: Opportunities and Threats of the (HR) organization.
- Benchmarking capabilities: Empuls helps HR teams benchmark internal engagement data against industry standards, which is especially useful when evaluating competitive positioning.
- Trend analysis support: The platform supports integrations with external HR data tools and allows exporting insights for deeper analysis of trends impacting employee engagement.
Step 3: Setting organization’s employee engagement objectives
The process of goal setting typically constitutes defining objectives that the organization wants to achieve in their people front – their culture, human capital, their people policies, etc. Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats can be a context to determine the objectives.
For example, an assumption such as - ‘Our competitors uses employee referrals as a strong source to recruit their talent. Referral employees tend to be the best and the most retained talent in the industry,’ is a threat that could lead an organization to consider ‘Improving employee referrals’ to be their HR goal.
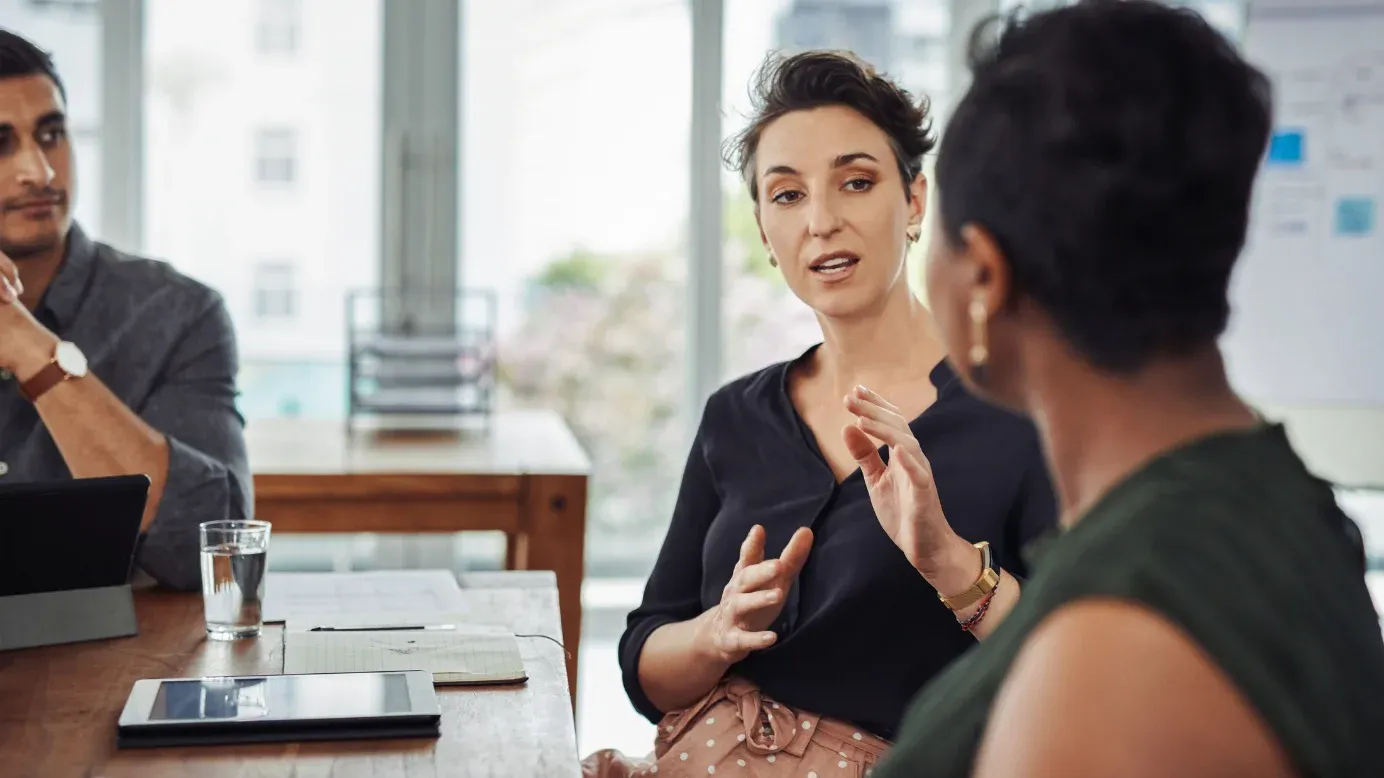
The S.M.A.R.T. methodology is predominantly used and is famously known for its ability to guide and help achieve goals. It draws the following guidelines.
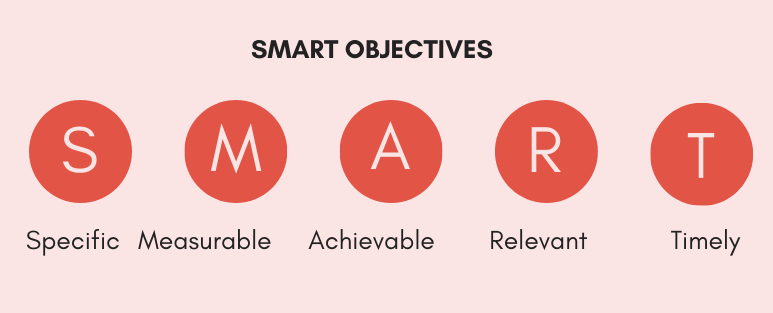
For example, a goal like ‘Improving the employee referrals of the company’ needs to be:
- Specific, for example, ‘We aim to improve our employee referrals.’
- Measurable, for example, ‘We aim to improve our employee referral %age from X to Y.’
- Achievable, for example, ‘We already are at X, thus achieving Y should be practical.’
- Relevant, for example, ‘Employee referrals are a double-edged sword that helps recruit new employees and that also indirectly indicates the employee Net Promoter Scores.’
- Timely, for example, ‘This increase in employee referrals needs to be within this financial year.’
The expected outcome of this step: A timeline and a priority list of SMART goals.
- Goal-driven campaigns: Empuls enables you to set up engagement initiatives with clear KPIs—such as recognition frequency, participation rates, or survey scores—aligning well with SMART goal frameworks.
- Customizable action plans: The platform helps align goals with actions by offering pre-built templates for engagement and recognition campaigns.
Step 4: Gap analysis
After setting the objectives, the next step is identifying the status quo of the variables and recognizing the distance that needs to be covered to achieve the planned goals.
This can be done using various tools, but a Fishbone (Ishikawa)analysis is a pretty simple and effective tool to drill down on the exact issues that need to be tackled to achieve these goals. The following is a snapshot of how Fishbone analysis (Lean Six Sigma) is done.
- Organize a cross-functional focus group.
- Allow them to identify the root causes (gaps) that affect achieving a prescribed goal.
- The root causes (gaps) can be categorized under ‘People’, ‘Processes’, ‘Policies’, etc., and further drilled down.
- Root cause analysis recommends understanding up to 5 levels of ‘Why’s of every cause to derive the exact root cause.
- List out the final list of root causes (Gaps).
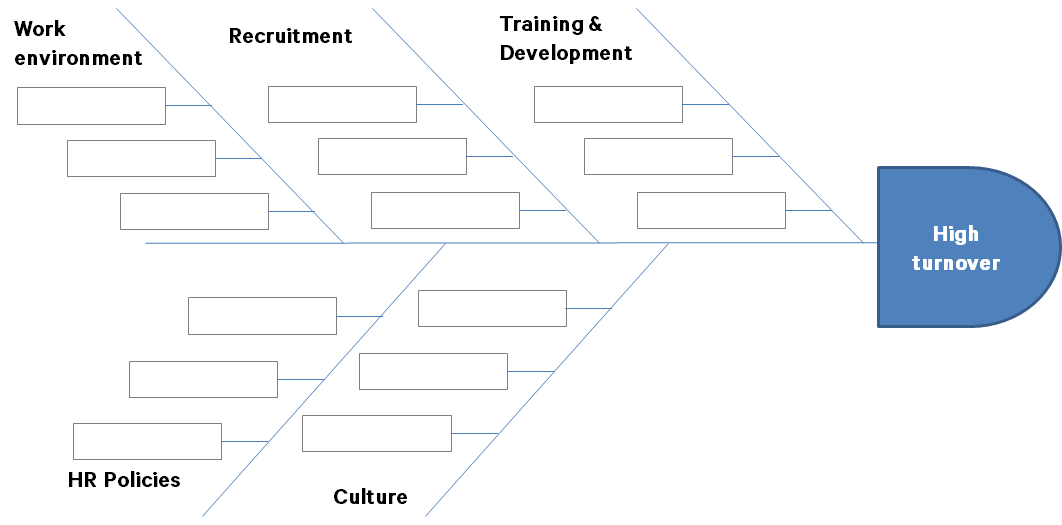
For example, a fishbone analysis of ‘Employee referral’ might bring out root causes such as ‘Pay inequities’, ‘Lack of employee insurance’, ‘insufficient employee feedback mechanisms, etc.
The expected outcome of this step: Qualitative /Quantitative Gaps in the existing process.
- Feedback loops & deep dives: Empuls allows for targeted feedback collection around specific themes (e.g., leadership, communication, well-being), aiding root cause analysis.
- Engagement heatmaps: Visual tools in Empuls help pinpoint departments or teams where gaps are widest, making it easier to conduct a “Fishbone Analysis” and prioritize interventions.
Step 5: Choice of strategy for action plan
Once the exact gaps in the process are listed, these need to be prioritized to execute. There generally are a number of paths to achieve goals, thus, selecting the right strategy for the action plan (or a gap to tackle) is a critical component of execution.
The fishbone analysis further allows screening and prioritizing these gaps using the following method:
Against each of the final list of root causes, evaluate the following:
- How does solving this gap impact the achievement of the goals? (Impact)) (Rate this on a scale of 1: signifying low impact to 10: signifying high impact)
- How financially feasible/ easy is it to work on solving this gap? (Ease) (Rate this on a scale of 1: very difficult to 10: very easy)
- Calculate the [Impact + Ease] value and tabulate it against the respective root cause
- Order the list of root causes (gaps) in decreasing order of the sum (A Pareto chart)
For example, a gap such as ‘Pay inequalities’ has low ease (because of the high cost involved) and a high impact, whereas ‘Insufficient employee feedback mechanisms’ have high ease (because the cost of implementation is low) but has a moderate impact. Depending on financial feasibilities and business priorities, leaders should further choose to tackle apt strategies.
The expected outcome of this step: An employee engagement program - the list of all the strategies that aim to address the top priority gaps.
- Customizable programs: Whether you're improving feedback channels or enhancing recognition, Empuls offers configurable workflows to design and deploy the right solution.
- Impact vs. effort planning: With data from Empuls, HR can prioritize strategies that balance high impact with low implementation cost, using insight-driven decision-making.
Step 6: Creating the team
The team that leads the implementation of the employee engagement process/program is important for its success. Depending upon the expertise a particular action plan requires - the team needs to have members who can contribute to it.
For example, a ‘Creating a robust employee feedback mechanism’ requires questionnaire design experts, technology experts (if automation is required), and HR experts (to lead and implement the plan - in a way that increases engagement.).
The expected outcome of this step: List of team members and their roles in each of the high-priority employee engagement action plan ideas.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Empuls includes internal communication features like a social intranet, announcements, and groups that foster cross-functional collaboration.
- Admin roles & permissions: Assign roles to different team members to lead or manage specific aspects of engagement campaigns.
Step 7: Measurement of performance
The 'measurability' aspect of the SMART goals provides metrics to be watched to evaluate the impact of the strategies to achieve goals.
For example, for the goal ‘Increasing employee referrals from X to Y’ - the actual percentage of employee referrals out of the total recruitment is the metric to be watched.
The expected outcome of this step: Value of the Metric used for measuring employee engagement.
- Real-time reporting: Measure engagement metrics like participation, feedback response rates, recognition frequency, and employee sentiment.
- ROI tracking: Empuls tracks the ROI of engagement initiatives, such as referral rates or retention improvements, helping validate impact.
- Custom KPIs: Build and monitor KPIs specific to your engagement goals directly within the platform.
Step 8: Analysing variance
The variance between actual and standard performance needs to be calculated to find a further gap in implementation. For example, if the strategies did not allow achieving expected Y% employee referrals within the stipulated time, these need to be re-evaluated and reconsidered.
Step 9: Taking corrective action
Re-evaluation of strategies should follow the entire flow of setting goals and selecting strategies (From Step 1 through 9). The reason why a plan is ineffective or a goal is not being achieved could be because of a wrong assumption throughout the course of planning.
For example, the reason why the goal ‘Improving the employee referrals of the company’ is not being achieved could be because of the following few of the many other plausible reasons.
- The target to be achieved was assumed wrong - 'Y' was too high a target.
- The timeline is too short.
- The fishbone analysis missed out on a major determinant, for example, ‘Referral rewards for the referring employees'.
- A miscalculation in the impact analysis. For example, the impact of ‘Pay inequities’ was lower than assumed.
- The team did not have an important skill required for implementation. For example, say questionnaire design in employee feedback implementation.
Empuls for employee engagement
Digital tools for employee engagement can help you create and grow a high-performance, high-engagement work culture. However, they work best only when the strategy for the action plan is created so that it emphasizes recognition and feedback and helps employees feel connected to their organization’s mission and values.
Using digital tools for employee engagement - like Empuls can help you design the best engagement plan to suit your organizational DNA. With Empuls, you can set:
- Recognition & rewards: Empuls automates peer-to-peer recognition and integrates rewards to reinforce positive behaviors.
- Employee wellness & communication: Encourage holistic engagement with wellness challenges and internal communications that reach employees at every level.
- Personalized engagement journeys: Tailor campaigns and communication based on employee lifecycle stages (onboarding, anniversaries, exits, etc.)
Empuls supports a data-driven, actionable, and scalable approach to employee engagement planning. It aligns with each phase of your action plan - rom diagnostics and goal setting to implementation and performance measurement - while also offering tools that boost culture, communication, and connection. Schedule a demo today and talk to our executives to find out more about Empuls. You can also start a 30-day free trial now.


















