Apple's Employee Engagement Strategies: Decoding their Secret
Learn all about Apple's employee engagement strategies and how it is core to their organizational purpose.
On this page
‘One of the keys to Apple is that Apple is an incredibly collaborative company.’ Steve abruptly pauses, smiles, and asks the interviewer.
‘Do you know how many committees we have at Apple?’
‘No’
‘Zero’ he replies, his eyes lighting up - starkly contradicting his fragile body.
We are organized like a start-up. We are the biggest start-up on the planet. There is tremendous teamwork at the top of the company, which filters down to having amazing teamwork in the rest of the company.
And teamwork is dependent on trusting the other folks that they will come through with their part without watching them all the time. We do that well. If you want to hire great people and let them stay working for you, you have to let them make many decisions, and you have to be run by ideas - not hierarchy.’
Steve Jobs spoke during his last interview with All Things Digital in 2010. Steve and Apple are everything that new-age business leaders and businesses envision to be – all for the right reasons.
Between September 1997, when Steve was rehired into Apple as the interim CEO, and August 24, 2011, when he retired, Apple’s stock grew by a staggering 100 fold.
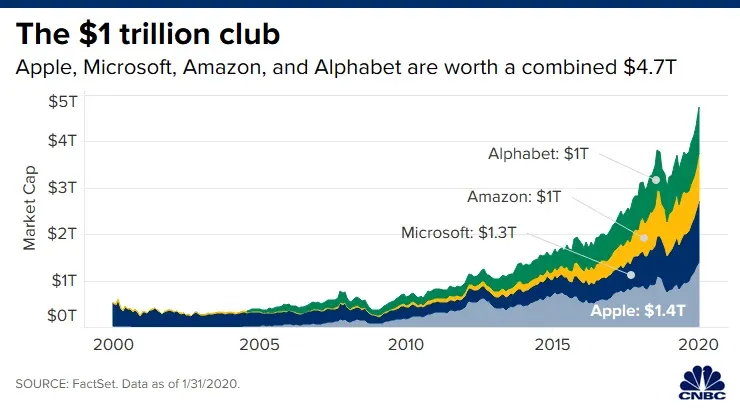
Apple was worth in 2020 a 1.4 Trillion billion USD, which is greater than the net revenues of Google, Amazon, and Microsoft - who are 3 of its closest contestants to be the world’s biggest brand.
As Steve denotes, the team at Apple is behind its overwhelming success, and this article inspects how the organization ensures this through its employee engagement strategies.
Apple’s employee engagement strategies
Apple’s approach highlights how innovation doesn’t stop at products—it extends to people too. Their focus on creativity, autonomy, and internal mobility sets the bar for modern engagement.
1. Alignment to organisational vision
Time and again, Steve Jobs was seen emphasizing his role at Apple was to spearhead their organizational vision.
Even decades later, during a D5 interview, he says, ‘my job is to get this ship [Apple] pointed in the right direction.’
The Executive Team (called ET) at Apple that runs each function owns the power of all decision making – not the board. Each of their Monday morning meetings is a powerhouse for alignment, during which they review the entire business to ensure all departments are on the same page.
They elaborately discuss products, processes, and innovation and take drastic decisions on each of these. Each participant executes this coherently as they agree upon a decision and disperse from these meetings.
2. Goal setting
Steve Jobs is famously known for genuinely obsessing over the smallest details. For instance, ‘Jobs even insisted that the matte black finish be coated onto the inside of the cube's case, even though only repairmen would see it’, quotes Walter Isaacson in his biography on Steve Jobs. This detailing even went into defining the roles of each employee.
Apple’s teams are divided into functions and not divisions, where these groups own expertise, innovation, and development of these functions entirely. The development process at Apple is organic, where these teams work on tasks in parallel, unified, and channelized by the ET meetings.
3. Innovation

iPhone, iPod, iPad, Air Pods, Apple Watch, Home Pod - The product innovations directly correlate to Apple’s staggering market share.
“Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower”, Steve famously quotes.
There are many ways Apple ensures the cycle of innovation is enabled, and the following are a few:
4. Product design
“Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works” says Steve Jobs.
Industrial Design is placed on top of all the other divisions at Apple. This ensures that the best-designed hardware prototypes get turned into actual products without being optimized and deformed by engineers.
Steve Jobs considered Jony Ive, the then Chief Design Officer of Apple, as a confidante in design because he felt Jony understands the operational power of design and that Apple is a product company.
5. Absence of P&L for all departments
Except for finance, no other department has a P&L at Apple because they believe that P&Ls are distractions to innovation. Since finance is a specialized function, having the technologists learn it and be controlled by the financial implications was thought to bring down their ability to innovate.
6. Office design
Apple Park at Silicon Valley includes a fitness center, an energy plant, and acres of apricot orchards. Every detail of the plan has been carefully examined to create the ideal environment for innovation and encourage collaboration between workers and between departments. Jonathan Ive, the former Apple's chief design officer, says that the building enables scores of people to connect, walk and talk.
7. Workplace design
Apple has spaces called pods for each activity an employee engages in during the workday - pod for office work, pod for teamwork, pod for socializing, etc.
These pods are distributed democratically – not even the CEO gets an incongruent pod. It is also a good way to provide flexible space for different types of work.
8. Customer feedback back
There is a reason why Apple has consistently taken a top spot in customer satisfaction rankings. Partly, this is because Apple relies on customer knowledge for innovation and improvement.
Feedback surveys have proven to be a beneficial way for Apple to gather customer insights. The company emails survey to customers immediately after they have made a purchase.
9. Diversity and inclusion
Diverse teams make innovation possible’, quotes Apple’s web page.
Apple believes that only a diverse group of people can create a product that can appeal to and work for a large group of people, it needs to be built by a diverse group of people.
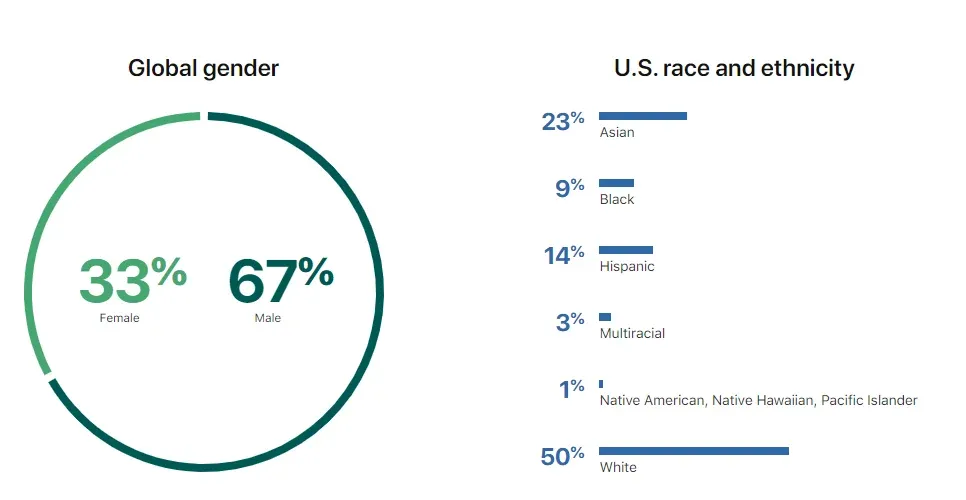
We’re working hard to include more diverse perspectives.’ Says Apple on their website and how in the last financial year (2018-19), over half of their new hires in the United States were from historically underrepresented groups in tech — women, Black, Hispanic, Native American, and Native Hawaiian & Other Pacific Islander.
10. Strong organizational structure
At the top, Apple has a Spoke-and-Wheel Hierarchy with Tim Cook at the center. The next tier of the corporate structure has function-based grouping, the senior vice presidents who report to Tim. The current hierarchy enables more collaboration among different parts of the organization and more autonomy for the divisional leaders.
The higher and lower tiers of the hierarchy have product-based and function-based divisions. There are senior vice presidents and vice presidents for different outputs or products. This helps to effectively manage specific products or product components that the company plans to deliver.
Corporate directives effectively control the business functions and product-based groups through this organizational structure. This facilitates the effective implementation of strategic management and helps create alignment throughout the organization.
11. Enabling teamwork
Product teams are small, with each group in charge of each product exclusively. The deadlines given to these teams are quick, and milestones are short. – based on the decision taken by the ET and learnings on the project's progress. Contrary to traditional product management, products are not processes from team to team – they are worked in parallel.
12. Driving employee experience through customer experience
They make wowing customers a priority for every frontline employee, not just a central team at headquarters. Instead of infrequent satisfaction studies, they ask their customers for feedback all the time. Employees extensively use this feedback for training and improving their effort.
To complement this effort, Apple also surveys its employees every few months. Instead of these efforts being that of the HR, employee engagement, a top priority is made a top priority for frontline managers and division heads.
The respective managers extensively review these employee surveys. Employee focus groups help identify critical issues and provide suggestions to help develop solutions to these issues. The teams quickly implement these recommendations. Over and above this, employees can also raise issues with upper management by posting on the Can We Talk section of the internal human resources website.
Both the survey efforts go hand in hand. Both require real-time learning, and the customer experience further nurtures the employee experience. Employees learn how to wow customers through customer surveys, and both employees and customers feel great in the process. This process is also called the Promoter Flywheel, and this has proven to have great financial performance.
13. Employee motivation
In 2015, Apple announced free shares to all of its employees, known as Restricted Stock Units, with initial grants ranging from $1000 to $2000. Even previous to 2015, Apple always had similar stock options available for their senior executives.
Stock options have been a great way to drive entrepreneurial ownership amongst employees to exhibit fruitful organizational citizenship behavior. This is also in tune with how Steve calls Apple the ‘world’s largest start-up’ where each employee works as a valid owner of their functions.
Apple is well-known to be providing employees with great perks.
Apple provides excellent discounts on Apple products anywhere in the 15 to 25 percent range. Apple frequently gives every employee gifts ranging from the iPod shuffle to the iPhone.
Even the storefront employees attend a considerable number of learning opportunities, team events, and activities, which allows them to keep their motivation high. Apple uses these events to reward and recognize its achievers.
“We have a tradition of ‘clapping out’ Apple employees when they leave the store at the end of shifts,” one of the Apple store managers said in an interview. “The Apple Store is an amazing place, like a community center. People go in with a sense of excitement. The employees know what they’re doing. There’s camaraderie.”
It is inspirational to watch the story of Apple’s success. Under Steve’s leadership, the organization has been an arena for product innovation and impeccability from the very beginning. This bespoke quality is replicated and generated in immense quantities. The fact that Apple is the largest manufacturer (out of not just electronic, all possible manufacturing in the world) – generating 2.6 times the revenue Microsoft generates out of their hardware, closely portrays the size of this quantity.
Only a rigorous and consistent engagement strategy can allow Apple to sustain this momentum. Quickly adapting to new demands of the market and delivering products that gratify the buying desires of the consumers, Apple has set itself apart. A strong organizational culture, visionary leadership, goal setting, innovation, and striving for quality are cornerstones for this organization’s exceptional journey.
Build an Apple-like engagement culture with Empuls
Apple’s success isn’t just the result of revolutionary products—it’s powered by people. From structured feedback loops and innovation-first mindsets to thoughtful recognition and inclusive perks, Apple has mastered the art of employee engagement. But you don’t need to be a tech giant to implement these practices.
Empuls empowers organizations of all sizes to create Apple-like engagement experiences. Whether you want to automate recognition, amplify employee voices through regular feedback, or offer meaningful perks that show you care—Empuls gives you the tools to build a culture that inspires, motivates, and retains top talent.
With features like:
- Employee surveys and actionable insights
- Recognition and rewards tied to company values and milestones
- A global perks and benefits catalog
- AI-powered nudges that prompt timely appreciation
- Social intranet features to foster alignment and collaboration
Empuls enables every organization to drive performance through people—just like Apple.
Conclusion: Behind great innovation is a great culture
Apple’s story isn’t just about sleek devices and market dominance—it’s about a workplace culture that empowers people to think differently, collaborate seamlessly, and bring their best selves to work every day. From Steve Jobs’ startup-inspired structure to today’s innovation-led teams, Apple has shown that employee engagement is not just an HR initiative—it’s a business imperative.
The company’s focus on alignment, recognition, feedback, and autonomy has created a blueprint that modern organizations can learn from. Whether you're building a high-growth startup or transforming an established enterprise, investing in your people is the surest way to unlock innovation, loyalty, and long-term success.
After all, the best products are made by the most engaged teams—and that begins with listening, appreciating, and empowering every employee, just like Apple does.


















