7 Ways HR People Analytics Transforms Workforce Strategy
HR people analytics empowers organizations with data-driven insights to enhance workforce planning, boost retention, and improve decision-making for a more efficient HR strategy.
Pada halaman ini
- Apakah analisis orang?
- Jenis analisis yang berbeza
- Analisis terbaik sebagai alat
- How is Empuls transforming people analytics with its powerful tools?
- Kawasan di mana analisis orang digunakan
- How to build a great people analytics strategy?
- Faedah orang analisis
- Menyimpulkan refleksi - Jalan untuk penggunaan yang meluas
- Soalan Lazim
Selama bertahun-tahun HR dianggap sebagai tugas untuk 'mengupah dan memecat' sumber, tetapi dalam tempoh masa, dengan kemajuan teknologi, perusahaan besar bercakap tentang kemungkinan untuk menggunakan data besar; yang akan membantu mereka dalam membuat keputusan berkesan mengenai kebajikan pekerja mereka dan organisasi.
Untuk ini, organisasi telah mula menunjukkan minat terhadap analisis orang dan melabur di dalamnya. Marilah kita memahami apa yang orang analisis dan bagaimana ia memberi kuasa kepada HR?
Program Sumber Manusia tidak lagi perlu berdasarkan penaakulan "lembut" tetapi harus seperti analisis dan data yang didorong oleh mana-mana disiplin pengurusan lain - Chris Argyris.
Peranan perunding HR telah berubah. HR bukan lagi 'tugas lembut' atau 'orang rakyat'. Kadar perkembangan teknologi telah mengarahkan profesional HR untuk menjadi lebih berpusatkan perniagaan dan celik teknologi.
Amongst other technological augmentations like AI in HR, Virtual Reality, Automation, Gamification, Cloud-based HR systems has had a major impact on HR professionals and has taken the HR world by a typhoon, transfiguring the way HR operates.
Dengan penggunaan sistem HR awan yang meluas, lebih banyak organisasi membiayai program untuk menggunakan data untuk semua aspek yang terdiri daripada perancangan tenaga kerja kepada keputusan orang dan peningkatan operasi.
Juga dinyatakan oleh Joash Narainsamy, Pakar Kesihatan Organisasi di ICAS Afrika Selatan.
"Analisis di tempat kerja boleh memberi gambaran tentang Pengurusan Ketiadaan, Presenteeism (sekarang tetapi tidak produktif), Pemerolehan dan Pengekalan Bakat, Keletihan dan Pengurusan Kemalangan, dan memberitahu anda dengan tepat di mana perniagaan anda berdarah dan apa yang perlu dilakukan."
Apakah analisis orang?
Analisis orang adalah proses meneliti data berkaitan orang yang ada untuk mengukur kecekapan program HR dan mengenal pasti corak untuk membuat keputusan perniagaan yang mendalam.
Dengan kata mudah, kita boleh mengatakan bahawa ia adalah satu proses yang merujuk kepada teknik analisis yang menggunakan teknologi, statistik, dan kemahiran kepada set data bakat yang besar yang membantu pihak pengurusan membuat keputusan perniagaan yang berkesan untuk organisasi dan juga untuk pekerja mereka dengan itu mempunyai peluang untuk mendapatkan pulangan yang lebih baik ke atas pelaburan mereka dalam perniagaan dan juga orang-orang yang mereka bekerja.
↠ 71% of companies regard people analytics as a topmost priority.
↠ 31% of companies rate it as very important.
↠ 8% of organizations stated that they have usable data.
↠ 9% believe they have a good understanding of which talent dimensions drive performance in their organization.
According to SHRM Research:
↠ 94% of business leaders believe that people analytics enhances the HR profession.
↠ Additionally, 71% of HR executives using people data analytics consider it essential to their organization’s HR strategy.
Analisis digunakan untuk pelbagai operasi perniagaan dan cabaran mereka. Pengambilan pekerja dianggap sebagai kawasan pertama dan terpenting, diikuti oleh bidang lain seperti perancangan tenaga kerja, mengukur prestasi pekerja, faedah pampasan, dan pengekalan.
Analisis rangkaian organisasi (ONA) dan "analisis interaksi" digunakan secara meluas untuk mengkaji tingkah laku pekerja untuk mengesan prospek baru untuk peningkatan perniagaan.
Jenis analisis yang berbeza
Menurut Model Kematangan Analisis Perniagaan Gartner, empat jenis analisis yang ditakrifkan digunakan secara meluas. Mereka adalah analisis deskriptif, analisis diagnostik, analisis ramalan, analisis preskriptif. Mari kita fahami ini secara terperinci.
1. Analisis deskriptif
Sama seperti rasuk atau dinding asas dianggap sebagai asas bangunan yang sama, Analisis Deskriptif dianggap sebagai tapak asas kecerdasan perniagaan.
Ia adalah peringkat pemprosesan data utama yang membentuk sinopsis data sejarah untuk membekalkan maklumat yang berguna dan mungkin menyediakan data untuk analisis selanjutnya. Ia terutamanya memberi tumpuan kepada soalan 'apa yang berlaku' mengenai isu-isu yang berkaitan dengan perolehan pekerja, bilangan pembukaan, masa untuk mengupah, laporan sewa baru, dan lain-lain.
2. Analisis diagnostik
Kami membentuk garis panduan terperinci tentang apa yang berlaku apabila kami melakukan kajian kes. Selepas kami menyiasat apa yang berlaku, kami cenderung menggali jauh untuk mengetahui mengapa ia berlaku. Begitu juga, analisis diagnostik memberi tumpuan kepada mengapa ia berlaku? Ia menggali terus ke kedalaman data untuk memahami sebab-sebab tingkah laku atau peristiwa tertentu.
3. Analisis ramalan
Ia adalah ranting analisis lanjutan yang digunakan untuk mengenal pasti dan memproyeksikan maklumat mengenai masa depan yang tidak diketahui. Kemungkinan dan peristiwa trending. Ia terdiri daripada banyak teknik statistik yang terdiri daripada pemodelan ramalan, pembelajaran mesin, perlombongan data, dan kecerdasan buatan yang menganalisis data semasa dan fakta sejarah untuk membuat unjuran tentang masa depan. Garis besar yang terdapat pada masa lalu dan data transaksi boleh digunakan untuk mengesan risiko dan peluang masa depan.
4. Analisis preskriptif
Ia adalah zon analisis perniagaan, dan ia memberi tumpuan kepada mencadangkan langkah-langkah yang mungkin untuk mengarahkan ke arah penyelesaian atau hasil yang berdaya maju. Ia dikaitkan dengan analisis deskriptif dan ramalan. Oleh kerana analisis deskriptif bertujuan untuk memberikan gambaran tentang apa yang berlaku, analisis ramalan membantu dalam meramalkan apa yang mungkin berlaku.
Analisis preskriptif menggunakan kecerdasan buatan dan pembelajaran mesin untuk memahami kesan masa depan. Ia bertujuan untuk menyediakan strategi terbaik berdasarkan situasi tersebut, dengan itu membantu perusahaan untuk mengurangkan risiko yang akan datang atau mencadangkan pilihan terbaik kepada perusahaan untuk memanfaatkan peluang masa depan. Analisis preskriptif digunakan dalam industri seperti perjalanan, minyak, dan gas, pengangkutan, dll.
Analisis terbaik sebagai alat
Analisis Ramalan boleh dianggap sebagai alat yang mengagumkan untuk perusahaan perniagaan di antara empat analisis yang disebutkan di atas. Sebabnya ialah ia mempunyai keupayaan untuk memberikan persepsi yang bermakna ke dalam bidang seperti pengurusan bakat, faedah pekerja, dan promosi atau membantu dalam meramalkan maklumat mengenai kejadian masa depan yang tidak diketahui.
Google uses employee performance data to compute suitable interference times to facilitate high-performing and low-performing employees' success. If you want the same result as Google, opt for Empuls.
How is Empuls transforming people analytics with its powerful tools?
Empuls empowers organizations with human analytics, providing data-driven insights into workplace culture, employee engagement, rewards, and perks. By analyzing people data analytics, HR leaders can optimize strategies, improve communication, and foster a thriving workforce.
1. Culture & values: Strengthening alignment and inclusivity
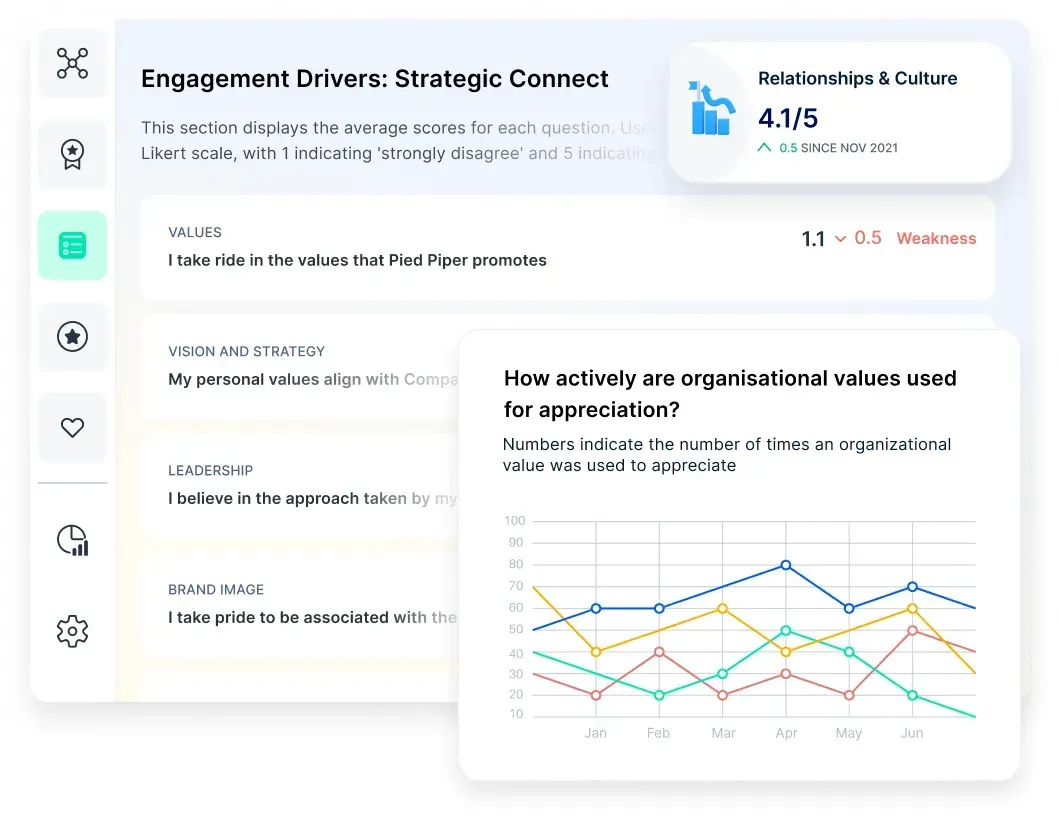
Track how well employees embrace core values through people analytics on values-based recognition. Monitor active discussions and sentiment trends to enhance collaboration. Use Empuls surveys to gauge cultural perception, identify gaps, and take proactive measures. Assess key aspects like DEI with measurable insights to build a more inclusive workplace.
2. Employee engagement: Driving performance and retention
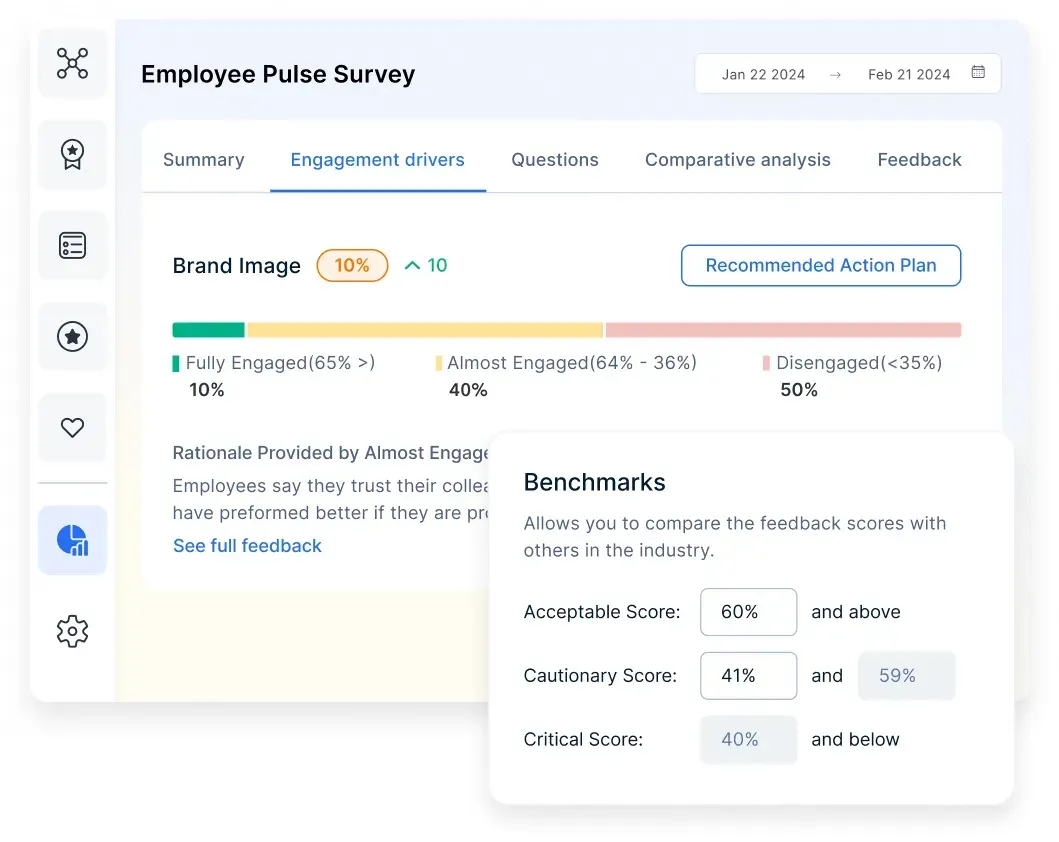
Measure engagement, loyalty, and workforce sentiment with eNPS and Pulse surveys. Leverage people data analytics to uncover trends in attrition, motivation, and team dynamics. Compare engagement levels with industry benchmarks and use actionable insights to strengthen retention strategies.
3. Reward & recognition: Fostering a culture of appreciation
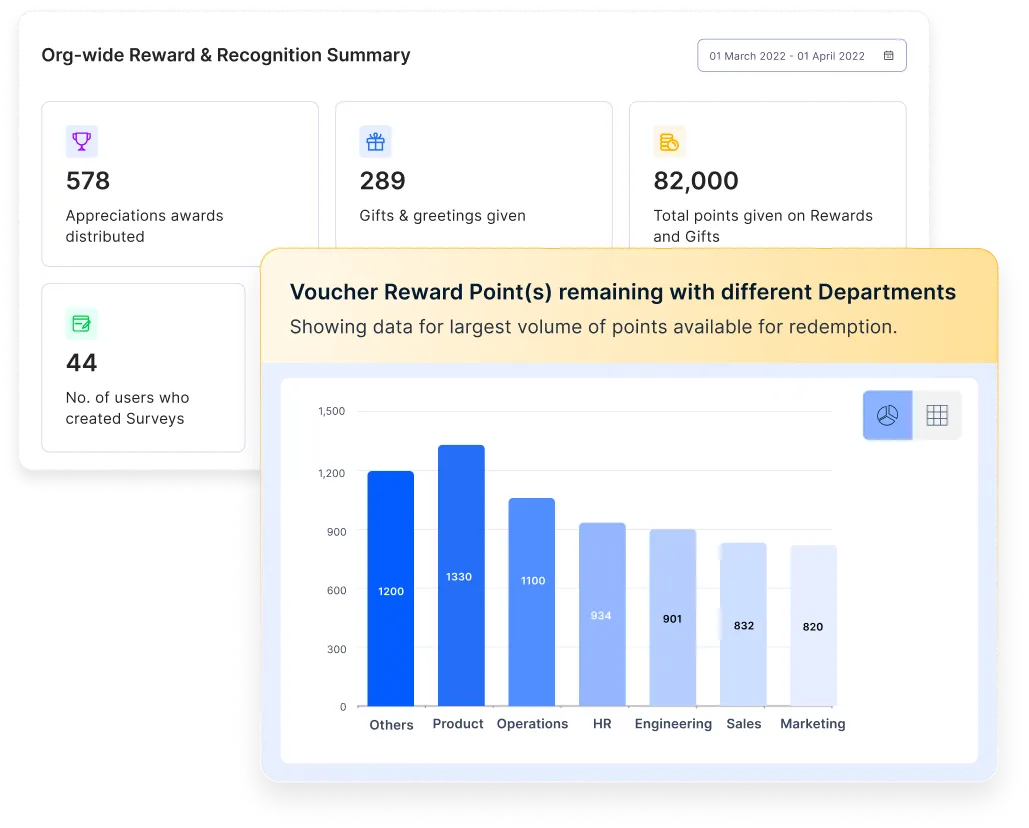
Analyze recognition trends across departments and locations to improve adoption and impact. Evaluate award effectiveness, monitor reward distribution, and track redemption patterns. Gain real-time insights into budget allocation, pending nominations, and overall rewards utilization for smarter decision-making.
4. Perks & wellbeing: Enhancing financial security
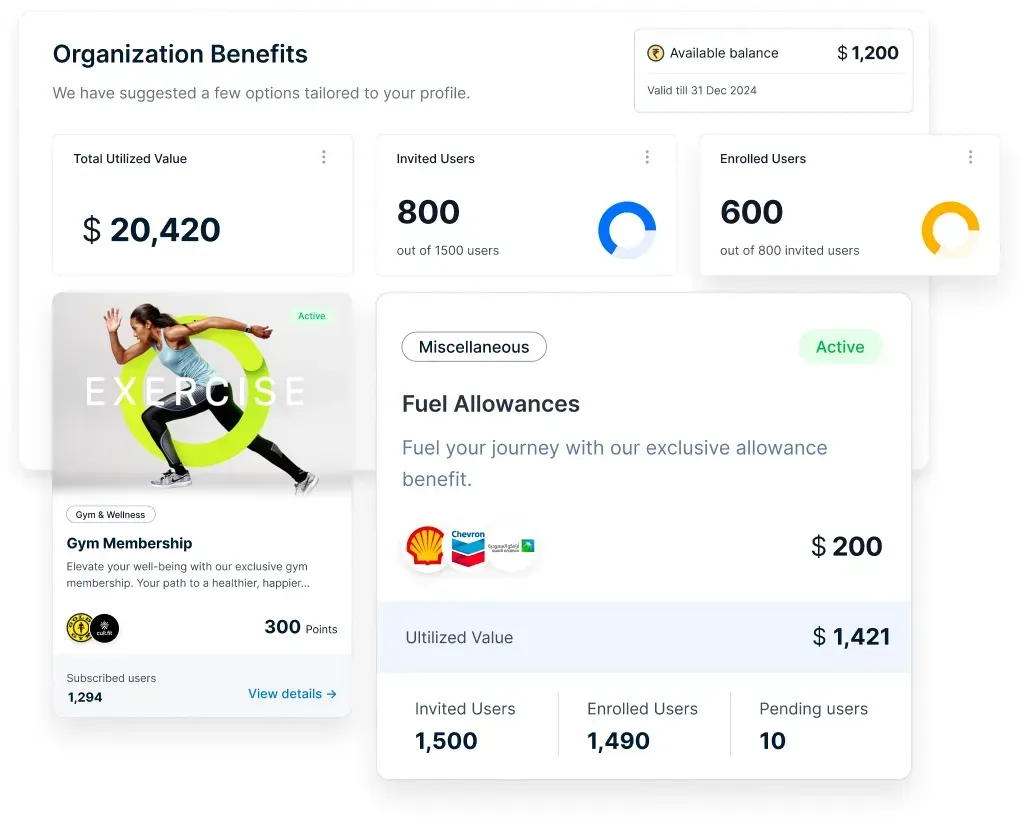
Track cost savings at both individual and organizational levels through employee perks. Provide employees with clear insights into monthly savings, enabling better financial planning. By leveraging recruiting people analytics, optimize benefits to attract and retain top talent.
Empuls enables HR teams to make data-driven decisions, using people analytics to enhance workplace culture, engagement, and rewards for a more motivated workforce. Schedule a call now to know how Empuls can help you out!
Kawasan di mana analisis orang digunakan
Perkembangan analisis manusia adalah di seluruh dunia dan tidak terhad kepada negara tertentu. Ia mempunyai penggunaannya dalam domain HR dan rangka kerja perniagaan. Bidang penggunanya mungkin berkembang dengan pelbagai pada tahun-tahun akan datang.
Analisis orang boleh dimanfaatkan dalam beberapa cara untuk meningkatkan fungsi syarikat. Untuk menamakan beberapa kawasan di mana analisis orang / boleh digunakan dalam perusahaan adalah:
- Pemerolehan bakat
- Mengambil pemohon yang tepat untuk mengurangkan berat sebelah dalam pengambilan pekerja
- Meningkatkan penglibatan pekerja
- Kesediaan tenaga kerja
- Mengukur budaya kerja, pengalaman pekerja, dan pengekalan pekerja.
Walau bagaimanapun, bidang HR seperti pengambilan, pengekalan / perolehan pekerja, dan prestasi pekerja adalah bidang teras di mana analisis boleh digunakan, dan organisasi boleh meraih faedahnya.
1. Pengambilan
Kemahiran prosedur stalking permohonan telah mengubah prosedur pengambilan. Penghakiman itu boleh berat sebelah selepas menemu bual pemohon tanpa mengira seberapa tepat maklumat berkaitan pemohon dibentangkan. Seperti yang dinyatakan oleh Sujee Saparamadu, Ketua Pegawai Eksekutif Orange HRM, dalam temu bual dengan Better Buys,
"Apabila anda melakukan perbincangan kecil sebelum wawancara, ini membawa kepada pengambilan bawah sedar pada kecenderungan pengesahan. Di situlah wawasan personaliti masuk ke dalam gambar.
Untuk membendung bias semasa bekerja melalui proses pengambilan, analisis orang boleh digunakan sebagai alat yang berguna untuk menjalankan penilaian yang berkaitan dengan pemohon. Kejelasan dari segi data mengenai ciri-ciri calon boleh berfungsi untuk pemahaman lain, seperti sama ada tingkah laku dan ciri keperibadian calon sesuai dengan budaya organisasi atau tidak.
Additionally, if all the data about the candidate is saved and being managed in a recruitment CRM software, it makes life easier for HRs to compare candidates and shortlist the best ones effortlessly.
2. Prestasi pekerja
Employee performance is where predetermined notions and prejudices are difficult to jiggle. People analytics allows HR to recognize probable fissures amongst employees within a particular department/team and what training and guidelines are required to compress and seal those fissures.
Menggali maklumat yang mendalam akan memberi organisasi intipati siapa yang akan menjadi penghibur yang tinggi dan rendah di kalangan pemohon yang baru diupah. Ini akan membantu pengurus berempati, terlibat dengan berkesan, dan menggalakkan pekerja untuk meningkatkan kemajuan keseluruhan organisasi.
3. Perolehan pekerja
Penggunaan analisis orang membantu mengenal pasti nisbah pengekalan pekerja. Dengan mengumpul beberapa data dan menembusi jauh ke dalam maklumat yang ada, perusahaan dapat memerhatikan tingkah laku pekerja dan memastikan tingkah laku pekerja yang akan meninggalkan / meninggalkan syarikat terhadap pekerja yang setia kepada syarikat.
Sama seperti perniagaan menentukan apa yang mendorong pengguna membeli keputusan yang sama, jenis pemahaman sedemikian membolehkan HR mendapatkan idea yang adil tentang apakah sebab yang membuat pekerja meninggalkan organisasi dan sebaliknya.
Daripada perbankan pada perasaan usus, adalah lebih baik untuk bank pada pandangan berasaskan bukti. Ini akan membantu HR membuat keputusan yang berkesan untuk meningkatkan pengekalan pekerja.
How to build a great people analytics strategy?
Terokai tujuh langkah ini untuk membina strategi analisis orang yang hebat:
1. Dapatkan bantuan daripada jejaka perniagaan
Fungsi (analisis orang) harus cukup berkebolehan untuk memberikan sokongan global dan bukan hanya analisis teknikal. Ia sepatutnya cukup sesuai untuk mengenal pasti masalah yang betul yang timbul semasa proses perniagaan.
Seseorang harus mendapatkan bantuan dan sokongan daripada pihak berkepentingan, sumber IT, eksekutif kanan, dan tidak melupakan jejak perniagaan.
2. Menubuhkan pasukan analisis yang kuat
Kejayaan analisis orang bergantung pada dan terdiri daripada pasukan di semua segmen perniagaan seperti kewangan, HR, dan lain-lain, dan data melintasi fungsi. Adalah penting untuk membina dan mewujudkan pasukan kepakaran pelbagai fungsi yang kuat dan rapat mahir dengan pengiraan data, visualisasi data, pengetahuan institusi, dan kemahiran nasihat supaya pasukan berkembang sebagai pasukan analisis perusahaan.
3. Kumpulkan HR dipacu data yang boleh dipercayai
Data yang tepat adalah asas kepada semua amalan analitik. Ketepatan analisis bergantung pada seberapa baik data dimasukkan ke dalam perisian. Seseorang perlu melabur dalam wang, masa, dan pelaksanaan pandangan yang boleh diambil tindakan yang diambil dari analisis untuk mendapatkan yang terbaik daripada analisis orang.
Langkah apa yang perlu diambil adalah penting untuk membuat keputusan sebaik sahaja organisasi menemui punca masalah melalui proses penilaian yang diperoleh daripada data statistik.
Langkah-langkah yang sesuai perlu diambil untuk memastikan kualiti data adalah sebahagian daripada setiap perbualan analisis. Elakkan menggunakan data yang tidak relevan kerana ia membawa kepada tafsiran kesimpulan yang salah dan mewujudkan pergolakan data.
4. Enhance analytics fluency
To choose a right to follow up the action, one must be intelligent enough to understand and interpret complicated data. For this, enterprises must implement and provide training on data governance programs that would provide training in implementing standard tools, standardization of reports and dashboards, etc., and prepare a cluster of important managers and knowledgeable HR stakeholders.
5. Membangunkan pelan hala tuju pelaburan dalam program analisis
Membangunkan pelan hala tuju pelaburan analitik untuk pelangi analisis yang luas. Pelaburan harus diusahakan untuk membentuk operasi perniagaan baru untuk organisasi dan bukan hanya pasukan teknikal dalam HR.
6. Memberi penekanan kepada tindakan dan bukan semata-mata penemuan
Untuk menambah nilai kepada program analisis orang, pasukan analisis harus cukup berkebolehan untuk memahami punca masalah dari maklumat yang diberikan dan memberikan penyelesaian yang terbaik dan paling sesuai.
7. Buat pelan data
Orang menganalisis bank mengenai bisection data dari operasi perniagaan, HR, dan sumber luar. Oleh itu, adalah perlu untuk mewujudkan pelan data untuk menyelaraskan / menggabungkan data yang teratur dan tidak teratur dari kedua-dua sumber dalaman dan luaran.
Faedah orang analisis
Persekitaran perniagaan yang sentiasa berubah telah menjadikan orang ramai analisis penting. Untuk menyokong fakta ini, berikut adalah faedah menggunakan analisis orang:
1. Memperkukuhkan membuat keputusan
Analisis orang membolehkan anda mengumpulkan maklumat dari sumber data yang luas yang membantu membuat keputusan yang berkesan. Ketika membuat keputusan, HR tradisional adalah subjektif.
Dengan pengenalan analisis orang, membuat keputusan subjektif telah berakhir. Analisis orang memberi anda data statistik yang membantu anda memahami masalah dan membuat keputusan yang berkesan untuk mengurangkan masalah.
2. Meningkatkan pengekalan
Kehilangan pekerja sedia ada boleh menjadi lebih mahal untuk organisasi daripada menyewa pemohon baru. Analisis orang membantu anda meningkatkan pengekalan pekerja. Seperti yang dinyatakan di atas, pemodelan ramalan berguna dan memainkan peranan penting pada masa akan datang.
Analisis ramalan membantu pengurusan mengetahui pekerja mana yang akan meninggalkan / meninggalkan organisasi. Dengan maklumat ini, mereka boleh mengambil langkah proaktif untuk mengekalkan pekerja dan menggalakkan mereka untuk kekal bersama organisasi.
3. Memacu akauntabiliti
Persembahan data adalah bahagian penting dalam pengiraan analisis orang. Menerima orang analisis bermakna menerima dunia penggambaran data yang mudah dan berkaitan. Data statistik sedemikian mudah ditafsirkan dan dapat difahami dalam konteks matlamat perniagaan strategik. Kejelasan ini meningkatkan akauntabiliti, kerana pekerja mengawal data.
Pekerja yang bertanggungjawab menunjukkan prestasi yang lebih baik dan dianggap lebih kepada aset perniagaan. Mencari cara untuk memacu akauntabiliti telah menjadi cabaran terbesar, dan analisis orang telah membiarkan pekerja yang bertanggungjawab memenuhi cabaran itu.
4. Meningkatkan kepuasan pekerja
Penglibatan pekerja telah menjadi isu utama dalam HR. Pekerja yang berpuas hati lebih produktif, teratur, dan lebih setia kepada organisasi yang mereka bekerjasama.
Analisis orang boleh memberi kesan yang baik terhadap kepuasan pekerja. Dengan analisis orang, pengurusan boleh mendapatkan idea tentang perasaan pekerja tentang bekerja di organisasi semasa mereka.
5. Sewa orang yang lebih baik
Salah satu faedah terbesar orang ialah mengambil calon yang lebih baik dan sesuai untuk jawatan tertentu. Analisis orang membantu anda membangunkan penilaian ramalan untuk prestasi berdasarkan prestasi teratas organisasi semasa.
Organisasi boleh menggunakan pengetahuan ini sambil menilai pemohon untuk memastikan mereka mengupah pemohon yang paling mungkin dilakukan dalam perniagaan mereka.
6. Menjimatkan masa
Dari penyumberan hingga pengambilan pekerja dan latihan untuk memupuk bakat adalah aktiviti yang memakan masa dan sepanjang masa dan usaha sia-sia dalam penempatan yang salah. Dengan analisis orang, majikan mendapat idea tentang orang dan program mana yang bernilai masa mereka dan yang tidak.
Akibatnya, analisis orang memberi anda masa tambahan untuk menghabiskan perkara-perkara yang mengarahkan hasil yang didorong oleh perniagaan.
Menyimpulkan refleksi - Jalan untuk penggunaan yang meluas
Banyak organisasi perlu membentuk fungsi analisis orang yang baik dan boleh dipercayai. Syarikat-syarikat yang telah memacu ke hadapan, dan organisasi-organisasi ini tidak mengehadkan fungsi analisis orang hanya kepada domain HR; tetapi telah memperluaskan fungsi analisis orang untuk bekerja di semua segmen perniagaan, termasuk kewangan, HR, dan operasi perniagaan, untuk meraih manfaat daripada kesan kuat fungsi terhadap prestasi perniagaan.
Analisis orang ditetapkan untuk menjadi elemen nukleus masa depan HR, dan perusahaan yang meletakkan kepercayaan dan kerahsiaan pekerja pada titik tengah usaha mereka akhirnya akan menjadi yang meraih nilai yang paling tinggi. Ia bersedia untuk menjadi jalan elektrik di hadapan.
Soalan Lazim
What is the scope of people analytics?
The scope of people analytics covers workforce optimization, talent acquisition, employee performance, engagement, retention, DEI initiatives, and overall HR strategy improvement through people data analytics.
What is another name for people analytics
People analytics is also known as human analytics, workforce analytics, HR analytics, or talent analytics.
What is the difference between HRIS and people analytics?
HRIS (Human Resource Information System) is a system that stores and manages employee data, such as payroll, attendance, and benefits. People analytics, on the other hand, analyzes this data to generate insights that help improve workforce planning, engagement, and decision-making.
What are the 7 pillars of people analytics?
The seven pillars of people analytics include:
- Workforce planning
- Talent acquisition and recruiting people analytics
- Employee engagement and experience
- Pengurusan prestasi
- Pembelajaran dan pembangunan
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI)
- Employee retention and attrition