Tasa de rotación de empleados: Causas, impacto y cómo reducirlo
Una elevada rotación de empleados puede alterar la productividad, aumentar los costes de contratación y rebajar la moral.
En esta página
- ¿Qué es la rotación de personal?
- Cómo calcular el índice de rotación de empleados
- Tasa media de rotación de empleados por sector
- ¿Qué significa realmente una elevada rotación de personal?
- Causas de la rotación de personal en el lugar de trabajo
- ¿Cómo reducir la rotación de personal?
- Medir el coste real de la rotación de personal
- Reducir la rotación de personal con Empuls
- Línea de fondo
El índice de rotación de empleados refleja la capacidad de su empresa para retener el talento. Aunque se espera cierta rotación, las bajas excesivas provocan pérdidas de productividad, costes de contratación y baja moral. Con una caída de las ofertas de empleo hasta los 8,7 millones y un mantenimiento de las bajas en 5,6 millones, las empresas deben centrarse en las estrategias de retención.
Una tasa de rotación saludable es de alrededor del 10% o menosSin embargo, el 75% de las empresas luchan por atraer y retener a los mejores talentos. Las empresas de alto rendimiento mantienen a sus mejores empleados con una tasa de rotación anual de empleados de alto rendimiento tan baja como el 3% o incluso cero.
Pero, ¿qué lleva a los empleados a marcharse? Las causas varían, desde una mala cultura del lugar de trabajo hasta la falta de crecimiento profesional y de conciliación de la vida laboral y personal, pero el impacto siempre es significativo.
Este artículo analiza las causas de la rotación de personal, cómo medirla y cómo reducirla con estrategias prácticas.
¿Qué es la rotación de personal?
La rotación de personal es el número de empleados que abandonan la empresa durante un periodo determinado, normalmente un año. Aunque la rotación de empleados suele abarcar el número total de empleados que abandonan una empresa, también puede calcularse por departamento o unidad.
La rotación de personal no se refiere únicamente a los empleados que abandonan voluntariamente la empresa. Por ejemplo, cuando se despide a un empleado por bajo rendimiento o mala actitud, eso cuenta como rotación de empleados.
Sólo que es involuntaria. Por tanto, parte de la rotación de personal es inevitable. Sin embargo, un repunte repentino de la rotación de empleados no lo es porque puede ser un reflejo del mal ambiente laboral que impulsa a los empleados a marcharse en primer lugar.
Las empresas con alta rotación son vistas como malos lugares para trabajar. En consecuencia, las empresas con mala reputación tienen dificultades para atraer a los mejores talentos.
Cómo calcular el índice de rotación de empleados
Saber si su empresa tiene un alto índice de rotación de empleados es crucial: es un indicador clave de la cultura del lugar de trabajo y de los problemas de retención. Si su rotación es significativamente superior a la de sus competidores, puede perder la batalla por los mejores talentos. He aquí cómo calcularlo con precisión.
1.Fórmula del índice de rotación (recomendada por SHRM):
Índice de rotación=(Número medio de empleados Número de bajas)×100
Identificar las bajas de empleados: Contar todas las bajas (voluntarias e involuntarias) durante un periodo determinado.
Determinar la plantilla media: Sume el número de empleados al principio y al final del periodo y divídalo por dos.
Aplique la fórmula: Divida el número de bajas por el número medio de empleados y multiplique por 100 para obtener el porcentaje.
Ejemplo de cálculo de la rotación de empleados
Empleados al inicio: 200
Empleados al final 180Empleados que se fueron 20
Número medio de empleados: (200 + 180) / 2 = 190
Índice de rotación: (20 / 190) × 100 = 10.5%
El cálculo de la rotación no siempre es sencillo. Debe decidir cómo contabilizar los empleados a tiempo parcial, los trabajadores temporales y los empleados de baja. La hoja de cálculo de la rotación de personal de SHRM puede simplificar este proceso garantizando cálculos precisos de la plantilla.
Por qué es importante la evaluación comparativa del sector
Su tasa de rotación no significa mucho a menos que la compare con la de sus competidores. Un índice de rotación "bajo" puede superar los estándares del sector, lo que indica un problema de retención. Investigar la tasa media de rotación de empleados por sector y ubicación ayuda a las empresas a comprender en qué punto se encuentran y qué mejoras son necesarias.
Por qué la rotación de personal es una preocupación creciente
La retención de empleados sigue siendo un reto en todo el mundo. Los estudios demuestran que la mitad de los empleados de EE.UU. se han planteado dejar su trabajo actual, lo que lo convierte en un mercado laboral competitivo. Las empresas que no abordan el problema de la rotación de personal corren el riesgo de perder a los mejores talentos en favor de empresas con una mejor cultura del lugar de trabajo y mejores estrategias de compromiso.
El seguimiento y análisis periódico de la rotación de personal es esencial para mejorar la satisfacción de los empleados y reducir las bajas innecesarias, garantizando así que su empresa siga siendo un empleador competitivo.
Tasa media de rotación de empleados por sector
Ahora que ya sabe cómo calcular el índice de rotación de empleados, su siguiente pregunta es: ¿qué constituye un índice de rotación bajo y alto? La respuesta dependerá de su sector.
Es difícil dar un índice ideal de rotación de empleados porque los factores específicos de cada industria también afectan a la rotación de empleados. Lo que puedo darte, sin embargo, son los trabajos con rotación de empleados y las industrias con alta rotación de empleados.
Vamos a sumergirnos:
1. Tecnología
Tech ha tenido la mayor tasa de rotación de empleados en los últimos años. En 2017, tuvo una rotación del 13,2%, según un estudio de LinkedIn. Eso es un 0,2% más que la tasa de rotación de empleados del comercio minorista (más información sobre esto más adelante). En años anteriores, el comercio minorista había encabezado sistemáticamente la lista de sectores con mayor rotación de empleados.
Dentro de la industria tecnológica, algunos sectores presentan los índices de rotación más elevados:
También hay puestos específicos de alta rotación. Por ejemplo, el puesto de diseñador de experiencia de usuario tuvo una tasa de rotación del 23,3%. Le siguieron el puesto de analista de datos y el de ingeniero de software integrado, con un 21,7% cada uno. Sin embargo, los altos índices de rotación de empleados en la industria tecnológica, en general, pueden tener más que ver con la competencia de personal.
A medida que aumenta la competencia en el sector por los escasos recursos, las empresas ofrecen salarios y beneficios más competitivos para competir, lo que hace que algunos empleados abandonen el barco cuando encuentran mejores oportunidades.
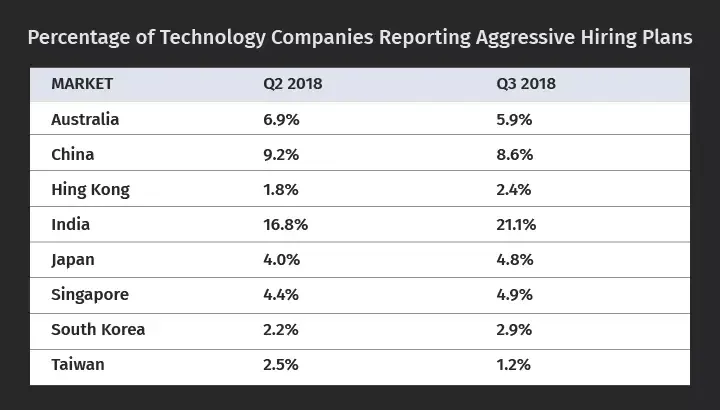
La tabla anterior, extraída del Informe trimestral sobre tendencias de la mano de obra de Radford Global Technology Survey muestra que, en particular, ha habido un repunte en el número de empresas que buscan contratar agresivamente, sobre todo en la India, donde el sector tecnológico está en auge.
En otras palabras, si bien hay una alta tasa de rotación en algunos campos de la tecnología, estos empleados que salen siguen consiguiendo trabajo en la industria tecnológica.
2. Industria minorista y de productos de consumo
Históricamente, la industria minorista y de productos de consumo ha tenido un alto índice de rotación de empleados. Según la encuesta de LinkedIndentro del sector minorista, los restaurantes tienen la tasa de rotación más alta, con un 17,2%:
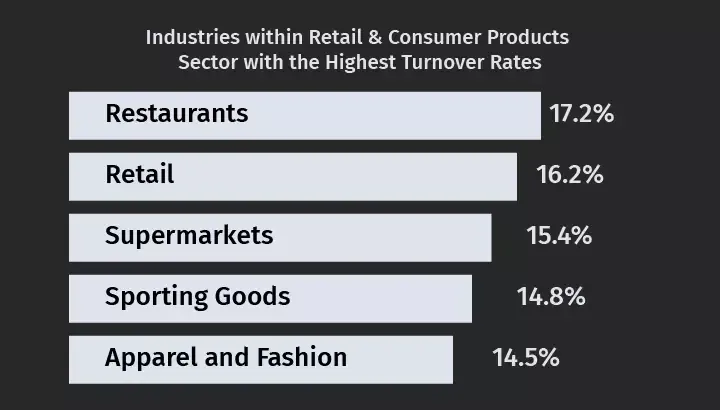
Dentro de la industria minorista, el personal de ventas al por menor tuvo la mayor tasa de rotación, con un 19,3%, seguido por los profesionales de los servicios de alimentación, con un 17,6%, y los profesionales de la hostelería, con un 17,0%.
Aunque es difícil decir cuáles son las principales razones de la rotación de empleados en el sector, el hecho de que los puestos con mayor rotación sean de bajo nivel y estacionales puede explicar muchas cosas. Además, el auge del comercio electrónico en el sector minorista hace que se necesite menos personal en las tiendas.
Esto se debe a que muchas funciones tradicionales del comercio minorista se han digitalizado y automatizado. Las compras en línea, los quioscos de autofacturación y la gestión automatizada de inventarios mediante software ERP de distribución han reducido la necesidad de contar con tanto personal en las tiendas.
3. Industria de los medios de comunicación y del entretenimiento
En tasas de rotación de empleados en los sectores de los medios de comunicación y el entretenimiento son constantes.
Ya sean periódicos, medios de comunicación online, deportes o viajes y turismo, la tasa de rotación de empleados es básicamente la misma según LinkedIn: del 13% al 13,2%.
No se puede decir lo mismo de los empleos en el sector cinematográfico. Los animadores tienen el mayor índice de rotación, con un 25,6%, seguidos por los artistas de 3D, con un 22,3%. Los especialistas en marketing ocupan el tercer lugar, con una tasa de rotación de empleados del 19,8%.
Los puestos de trabajo de alta rotación, según los datos, se basan en su mayoría en proyectos (o tienen un principio y un final claros, según la duración del rodaje de una película, por ejemplo).
La elevada tasa de rotación podría explicar el éxodo de empleados. Si es así, estas estadísticas deben tratarse con cierta cautela, ya que no es una medida exacta de la rotación de los empleados.
¿Qué significa realmente una elevada rotación de personal?
Hay muchas, muchas razones por las que los empleados abandonan su organización a un ritmo elevado - puede ser diferente para cada empresa. Pero hay algunos factores comunes que querrás analizar y que suelen ser la causa de que los empleados se marchen.
1. Remuneración o prestaciones deficientes
Si sus empleados trabajan tan duro como los de la competencia, pero no reciben el mismo nivel salarial o de prestaciones, es una razón de peso para que se marchen. Y con la popularidad de sitios como Glassdoor, los empleados de hoy en día tienen mucha información sobre lo que ganan sus compañeros en otras organizaciones.
Al fin y al cabo, los empleados aceptan un trabajo por muchas razones, pero la más importante es ganar dinero para mantenerse a sí mismos y a sus familias. Si no sienten que pueden hacerlo contigo o se sienten mejor en otro sitio, es más probable que se marchen.
2. Cultura negativa en el lugar de trabajo
¿Están sus empleados estresados, sobrecargados de trabajo, poco valorados o sometidos a demasiada competencia malsana? La cultura de su lugar de trabajo tiene un impacto significativo en la retención de los empleados.
Si los empleados sienten que su organización demuestra a través de la cultura del lugar de trabajo que usted no se preocupa por ellos como personas, es probable que pronto se dirijan a la salida. Eso puede significar una cultura de exceso de trabajo, infravaloración y una cultura de límites deficientes, por lo que los empleados trabajan a todas horas o cultura de comportamientos desagradables o perjudiciales.
Los empleados pasan la mayor parte de la semana en el trabajo: ¿ha creado una cultura de apoyo en la que puedan dar lo mejor de sí mismos o una en la que no puedan esperar a salir por la puerta al final del día?
3. Escasas oportunidades profesionales
Puede que tenga un salario competitivo y una gran cultura de trabajo, pero se da cuenta de que los empleados se marchan más a menudo de lo que le gustaría. Podría ser la falta de oportunidades profesionales. Si los empleados no sienten que hay un camino hacia el éxito a largo plazo en tu empresa, eso no es muy alentador.
Quieren oportunidades para aprender nuevas habilidades, asumir nuevos retos y hacer crecer sus carreras. Eso no significa que tenga que ascender a todos los empleados cada año, no es una expectativa razonable.
Pero puede ayudar a analizar detenidamente el tipo de planes y oportunidades de desarrollo profesional que ofrece a sus empleados: ¿hay margen de mejora, especialmente para sus talentos más prometedores? Ayudarles a ver un futuro claro y a planificar cómo llegar a él puede animar a los empleados con talento a quedarse y seguir contribuyendo a su empresa.
4. Cuando la rotación es saludable
Dicho esto, no toda la rotación de personal es mala. Un nivel saludable de rotación aporta sangre fresca e ideas a su organización. Las nuevas contrataciones pueden aportar nuevas formas de ver los viejos problemas y mejorar el funcionamiento de su organización. En un mundo tan cambiante como el actual, no queremos que las cosas se estanquen, así que no nos fijemos como objetivo una tasa de rotación cero.
Además, a veces se desea que los empleados que no se adaptan bien a sus funciones o a la cultura de la empresa salgan de la organización y encuentren un lugar o una función que les convenga más. Este tipo de rotación es saludable y a veces debería producirse en lugar de retener a personas que simplemente no funcionan.
En resumen, no intente deshacerse de toda la rotación de empleados: asegúrese de que se encuentra en un nivel saludable y de que se produce por las razones correctas.
Construir una cultura que los empleados no quieran abandonar
Los empleados se van cuando no se sienten valorados. Empuls hace que el reconocimiento, las recompensas y las conexiones en el lugar de trabajo se realicen sin esfuerzo, aumentando la retención y la satisfacción laboral.
Causas de la rotación de personal en el lugar de trabajo
Ya he mencionado que cierta tasa de rotación de empleados es inevitable. Cuando los empleados se jubilan, por ejemplo, eso no está bajo el control de la empresa. Lo mismo puede decirse de los empleados que deciden cambiar de carrera.
Sin embargo, hay razones para la rotación de personal sobre las que las empresas pueden hacer algo. Veámoslas en esta sección:
1. Falta de crecimiento
Nadie quiere quedarse atrapado en el mismo trabajo de siempre, haciendo la misma rutina de siempre. De hecho, según Business2Community, las oportunidades de desarrollo profesional ocupan el tercer lugar entre las ofertas no monetarias de la empresa que hacen que los empleados se queden.
Si quieres que tus empleados se queden a largo plazo, asegúrate de dejarles claro desde el principio que tienen un futuro en la empresa si se esfuerzan mucho.
Recuerde siempre que sus empleados no son robots que no tienen planes. Las personas tienen objetivos profesionales y quieren progresar en la carrera que han elegido. Si el trabajo que tienen ahora no les ayuda a alcanzar esos objetivos, dejarlo no será tan difícil.
2. Demasiado trabajo
Si preguntas a los antiguos empleados de las empresas con alta rotación por qué se fueron, el exceso de trabajo es probablemente una de las razones que te darán. A todo el mundo le gusta un trabajo que pague las facturas, pero no si le lleva al estrés y, lo que es peor, incluso a la enfermedad.
Demasiado trabajo provoca agotamiento y eso, según la Harvard Business Reviewcuesta entre 125.000 y 190.000 millones de dólares al año en gastos sanitarios en Estados Unidos. Sin embargo, los costes reales para la empresa pueden ser aún mayores, con una baja productividad como resultado de la pérdida de talento.
En otras palabras, todas las empresas deberían respetar también el tiempo de sus empleados. Hay una razón por la que los empleados utilizan una aplicación de reloj de fichar para entrar y salir del trabajo. Una vez que el reloj marca las 5 de la tarde, básicamente pueden hacer lo que quieran. Pero eso también significa que tendrían que estar en la oficina exactamente a las 9 de la mañana del día siguiente.
3. Falta de reconocimiento
Dar crédito a quien lo merece es clave para retener a los empleados. Según The Balance Careers el 55% de los empleados creen que el reconocimiento de los empleados les hará sentirse valorados. De los encuestados en el estudio, el 58% también afirmó que el reconocimiento de los empleados mejora el compromiso de los empleados en la empresa, un elemento crucial para retener a los empleados.
También está la relación entre el reconocimiento y la productividad. Según Gallup, el 69% trabajaría más si sintiera que sus esfuerzos son reconocidos. Eso se traduce en una mayor productividad de la empresa en general y en un aumento de los beneficios.
4. Poca oportunidad de decidir
Los directivos deben gestionar a sus equipos, pero eso no significa que deban "asfixiarlos". Por supuesto, no lo digo en el sentido literal de la palabra. Quiero decir que no deben microgestionar a los empleados hasta el punto de que ya no puedan hacer nada sin la aprobación del jefe.
Si los empleados tienen pocas oportunidades de decidir, la moral se ve muy afectada. Esto se debe a que se frustran con la pérdida de autonomía y pierden el deseo de hacer un esfuerzo adicional cuando se les asigna una tarea. Y cuando hay baja moral, hay baja productividad.
Cuando a los empleados se les da poca oportunidad de decidir, también se vuelven demasiado dependientes del directivo; dejan de pensar con originalidad y de crecer.
5. Mala selección de empleados
A veces los empleados abandonan las empresas porque está en su ADN hacerlo. Aunque las empresas no pueden hacer nada con respecto al ADN de una persona, sí pueden controlar a las personas que contratan. RRHH debe contratar, no sólo al candidato con las aptitudes para el puesto.
También debe fijarse en la actitud y los valores del candidato. Si no coinciden con los valores de la empresa, aunque el candidato sea el mejor para el puesto en cuanto a habilidades, es mejor ir a por el siguiente que probablemente sea feliz en su oficina. Porque cuando esa persona es feliz, es más probable que se quede.
¿Cómo reducir la rotación de personal?
Ahora que conoce las principales razones de la rotación de personal, vamos a discutir las estrategias para reducir la rotación de personal y evitar que sus empleados se vayan:
1. Garantizar una trayectoria profesional clara para los empleados
Como responsable de RRHH, también debe colaborar estrechamente con los directivos de la empresa para identificar a los empleados con potencial. Una vez identificados, su supervisor inmediato debe orientarles para que puedan tener las habilidades necesarias para crecer. La idea es ayudarles a cumplir los requisitos necesarios para ascender en la empresa.
Por su parte, proporcione a los directivos y empleados potenciales el apoyo necesario que necesitan. Puede, por ejemplo, patrocinar cursos de formación y seminarios. Organice actos con altos cargos de la empresa como ponentes de recursos y los empleados también como público.
De este modo, sus empleados sabrán más sobre cómo empezó la dirección en la organización y cómo, con trabajo duro, crecieron y alcanzaron el éxito.
2. Garantizar un buen equilibrio entre trabajo y vida privada
No lo hagas todo con tus empleados. Recuérdales que se tomen sus descansos para comer. Llévales de vez en cuando de excursión a la empresa. Organice eventos sociales en la oficina. Déjales claro que, aunque la empresa valora la productividad, no lo hace a costa de su salud.
Asegúrese de controlar la carga de trabajo a los empleados. Si un miembro del equipo está atascado de trabajo, algunas de las tareas pueden asignarse a otros miembros del equipo que puedan hacerlas igual de bien. Delegue, para que ningún miembro del equipo se vea sobrecargado de trabajo y se sienta tan frustrado que se marche.
3. Mejorar el compromiso de los empleados a través de la comunicación
La falta de comunicación y transparencia alimenta la falta de compromiso, haciendo que los empleados se sientan desconectados de la misión de la empresa. La intranet social deEmpuls y las herramientas de encuesta de Empuls ayudan a cerrar esta brecha creando un espacio de comunicación interactivo y abierto en el que los empleados pueden compartir sus opiniones, participar en debates y mantenerse informados.
Las encuestas periódicas proporcionan información en tiempo real sobre el sentimiento de los empleados, lo que ayuda a los responsables de RR.HH. a abordar las preocupaciones antes de que se conviertan en rotación. Cuando los empleados se sienten escuchados e implicados, están más comprometidos y es menos probable que busquen oportunidades en otros lugares. Una plantilla conectada es una plantilla retenida.
4. Reconocer y recompensar a los empleados de vez en cuando
Es más probable que los empleados se queden cuando se sienten valorados por sus contribuciones. El agradecimiento regular -ya sea mediante reconocimiento verbal, primas u oportunidades de desarrollo profesional- crea un entorno de trabajo positivo en el que los empleados se mantienen motivados y comprometidos. Reconocer los logros no sólo sube la moral, sino que también refuerza los valores de la empresa y fomenta el alto rendimiento.
Aquí es donde Empuls ayuda a las organizaciones a construir una cultura de reconocimiento con agradecimiento en tiempo real, recompensas personalizadas y celebraciones de hitos. Con funciones como el reconocimiento entre iguales, los incentivos automatizados y las recompensas por aniversario de servicio, Empuls garantiza que los empleados se sientan reconocidos en cada etapa de su trayectoria. Al hacer del reconocimiento una parte integral de los flujos de trabajo diarios, las empresas pueden mejorar el compromiso, fortalecer la lealtad y reducir significativamente la rotación.
5. Dar crédito a quien lo merece
Siempre es una buena idea reconocer el trabajo duro. Cuando las empresas hacen esto, hacen que los empleados se sientan valorados y motivan a los empleados a trabajar aún más. Como RRHH, puedes, por ejemplo, organizar un día especial de reconocimiento para los empleados que hayan destacado durante un periodo determinado.
Por ejemplo, reconozca en un evento para toda la empresa al vendedor que más productos haya vendido durante el primer trimestre del año. O dé permisos de vacaciones extra a esa persona que nunca llegó tarde al trabajo. Si puede, también puede ofrecer recompensas monetarias. Sé creativo.
Busque tendencias en programas de recompensas para empleados e inspírese. Si da crédito a quien lo merece, mantendrá a sus empleados contentos y comprometidos. Y dejar la empresa por ellos será impensable.
6. Diga a los directivos que no microgestionen
No me malinterpreten. Los jefes prácticos son estupendos. Sin embargo, lo que las empresas no quieren son directivos que sean demasiado prácticos y sus compañeros no puedan hacer nada sin ellos. Como responsable de RR.HH., informa a tus jefes de cómo le gustaría a la empresa que se hicieran las cosas.
Aunque la gestión de equipos es necesaria, no debe llegar al punto de que todo el flujo de trabajo se atasque porque los jefes tengan que aprobarlo todo. Diles que den a los empleados cierto margen para decidir las cosas. De este modo, los empleados sentirán que tienen algo que aportar. Y desarrollarán su capacidad de decisión.
7. Hacer bien el proceso de selección
No se limite a pasar por el proceso de selección cuando quiera cubrir un puesto en la empresa. El proceso de selección existe para que las empresas se ahorren contratar a candidatos que no encajan bien en la empresa. Así que tómese su tiempo y realice la entrevista correctamente con un proceso eficaz de gestión del talento.
Formular preguntas pertinentes. Se trata de calibrar las aptitudes del candidato Y su actitud y personalidad. Contratar a alguien sólo porque fue el primero en solicitar el puesto con las aptitudes requeridas nunca es una buena idea. Hay que esperar a la persona adecuada. No hay que forzar a un candidato a ser la persona adecuada para poder anunciar que el puesto está cubierto.
8. Ofrecer remuneración y prestaciones competitivas
El salario desempeña un papel clave en la retención, pero no se trata sólo de ofrecer un sueldo base competitivo. Hoy en día, los empleados esperan unas prestaciones completas que vayan más allá del sueldo. Las empresas deben ofrecer planes de asistencia sanitaria, beneficios de bienestar, bonificaciones basadas en el rendimiento y beneficios complementarios libres de impuestos para aumentar la seguridad financiera y la satisfacción laboral.
Además, prestaciones como el reembolso de matrículas, las ayudas para guarderías y las cuentas de gastos flexibles hacen que los empleados se sientan valorados y respaldados, lo que aumenta su compromiso con la organización. Las empresas que invierten en paquetes retributivos completos crean un lugar de trabajo en el que los empleados se sienten económicamente estables y motivados para quedarse.
Medir el coste real de la rotación de personal
Pregunte a cualquier empleado, profesional de RR.HH. o gurú empresarial y le dirá que sí, que la rotación de personal es mala. Por supuesto, tiene sentido: ¡que los empleados abandonen tu empresa no es una buena señal!
No hace falta un MBA para saberlo. Pero poca gente conoce el coste real de la rotación de personal. Y eso es un problema, porque la rotación cuesta a las empresas mucho más de lo que creen.
Si no sabe lo que le está costando un exceso de rotación, no comprenderá la urgencia de solucionar el problema.
Echemos un vistazo a los costes reales de una baja retención para su cuenta de resultados.
1. El coste financiero
El coste de la rotación de personal más fácil de calcular es el peaje financiero que supone para su empresa. A la larga, los empleados son un activo para su empresa, pero al principio de su carrera con usted, tienen un coste.
El reclutamiento, la contratación y la formación conllevan costes monetarios que no se pueden eludir. Hay muchos datos disponibles sobre cuánto cuesta sustituir a un empleado que se marcha, en función de su nivel y del tiempo que lleve en su puesto.
Entonces, ¿cuánto cuesta sustituir a un empleado que se marcha en dólares reales? Hay muchas maneras de calcular el coste. Sin embargo, un buena referencia es el 50% del salario de los empleados principiantes, el 125% del salario de los empleados de nivel medio y más del 200% del salario de un alto ejecutivo. Eso es mucho. Como mínimo, son decenas de miles de dólares que hay que gastar cada vez que un empleado abandona la empresa.
Por supuesto, esta tasa varía según el sector y la empresa: puede calcular el coste exacto de rotación de su empresa con esta calculadora de hoja de cálculo de la SHRM. Pero ese coste fiscal, por impresionante que sea, no es el único en el que incurres con cada salida.
2.El coste del conocimiento
Cada año que un empleado trabaja para su empresa, adquiere más conocimientos. Aprenden cosas como los procesos y procedimientos necesarios para hacer las cosas como las hace su empresa.
Adquieren experiencia trabajando con sus clientes y entablan relaciones con ellos. Establecen relaciones entre ellos. Pasan de necesitar formación a ser capaces de formar a otros empleados. Maduran hacia puestos directivos. Aumentan su inestimable conocimiento institucional y del sector.
Cuando se van, todo eso también se va. A diferencia de herramientas como impresoras, sillas de oficina o la nevera de la sala de descanso, los empleados son un activo que se revaloriza. Aumentan su valor cada año que permanecen en la empresa, gracias a todo lo que aprenden y aplican cada día.
Por tanto, si pierde regularmente empleados que se van a la competencia al cabo de dos o tres años, también está perdiendo ese aprendizaje a largo plazo que los empleados absorben y transmiten a los recién contratados. También se pierden las valiosas relaciones que los mejores empleados desarrollan con los clientes.
Puede acabar perdiendo uno o varios clientes junto con un empleado, y eso puede ser devastador para su empresa. No puede permitirse que sus estrellas se vayan por motivos evitables.
3.El coste moral
Reconozcámoslo: si sus empleados abandonan la empresa al cabo de un par de años, o de un par de meses, es probable que algo vaya bastante mal en algún aspecto de la experiencia del empleado. Construir una moral de empleados fuerte no es fácil cuando los trabajadores siempre están saliendo por la puerta.
Los altos índices de rotación de personal pueden ser tanto una causa como un síntoma de un bajo nivel de compromiso y moral de los empleados. Si a los empleados no les gusta venir a trabajar cada día y no se sienten comprometidos con su trabajo, es más probable que lo abandonen.
Y probablemente todos hemos tenido la experiencia de estar en un equipo en el que una persona tras otra se va, y empieza a parecer bastante ominoso.
Los empleados que se quedan tienen que asumir el relevo, lloran la pérdida de relación con el compañero que se ha ido y empiezan a preguntarse si ellos también deberían marcharse. Esto puede provocar un círculo vicioso de rotación cada vez mayor hasta que sólo queden los empleados más nuevos y con menos experiencia, que no tienen adónde ir.
Reducir la rotación de personal con Empuls

Una elevada rotación de empleados no sólo repercute en los costes de contratación, sino que afecta a la moral del equipo, la productividad y la cultura general de la empresa. Los empleados no se van sólo por un mejor salario; se van cuando se sienten infravalorados, desconectados o no escuchados. Empuls ayuda a las empresas a crear un entorno en el que los empleados se sientan motivados para quedarse.
En lugar de reaccionar cuando los empleados dimiten, Empuls permite a las empresas captar y retener el talento de forma proactiva:
- Reconocimiento y recompensas: Una cultura de reconocimiento fomenta la lealtad. Con Empuls, los empleados reciben el reconocimiento oportuno por sus contribuciones, lo que les hace sentirse valorados.
- Feedback y encuestas en tiempo real: Es fundamental saber qué necesitan los empleados antes de que se desvinculen. Las encuestas de compromiso deEmpuls descubren preocupaciones ocultas y proporcionan información práctica.
- Intranet social para la conexión: Un lugar de trabajo conectado reduce el aislamiento y refuerza la cultura de la empresa. La intranet social deEmpuls de Empuls fomenta la comunicación abierta y la colaboración, incluso en equipos remotos.
- Ventajas personalizadas para los empleados: Ofrecer beneficios que se ajusten a las preferencias de los empleados -como programas de bienestar, oportunidades de aprendizaje o recompensas por hitos- mejora la satisfacción laboral y la retención.
Cuando los empleados se sienten escuchados, apreciados y comprometidos, eligen crecer dentro de la empresa en lugar de buscar en otra parte. Empuls proporciona las herramientas adecuadas para crear un lugar de trabajo en el que los empleados permanezcan, prosperen y contribuyan al éxito a largo plazo.
Línea de fondo
Nadie piensa que los altos índices de rotación de empleados sean buenos para el negocio. Pero hasta que no sepa realmente cuánto le cuesta a su empresa cada empleado que se marcha en dólares de contratación y formación, en conocimientos institucionales perdidos y en moral de equipo, no podrá empezar a desarrollar soluciones eficaces. ¿La buena y la mala noticia?
La mayor parte de la rotación de personal se puede evitar. Una vez que haya calculado el coste real de perder empleados, podrá empezar a elaborar estrategias para retenerlos. Y entonces estará en el camino de construir una empresa sostenible y de éxito en la que a sus empleados les encante trabajar.













